探討噬脂作用:從機轉到神經退行性疾病
Targeting lipophagy: from mechanism to neurodegeneration
Our goals are to address 1. Why neuronal lipophagy, the selective turnover of lipid droplets through the autophagy pathway, was found to be neuro-protective, and 2. The molecular mechanism behind neuronal lipophagy activation. We would like to utilize the knowledge gained here to devise schemes to manipulate lipophagy for alleviating neuronal disorders. Our efforts will allow one to link dysfunctional lipid metabolism with diseases, understand lipophagy at the molecular level, and allow the eventual manipulation of lipophagy for neuro-protection.
本計畫目標為釐清脂噬作用為何具備保護神經之功能,及其活化的分子機轉。藉由釐清其機轉,本計畫希望能增進相關知識,因此找到操弄脂噬作用的節點,以作為減緩神經退化之後續運用。藉此計畫,我們得以連結脂質代謝失衡與神經退化、理解脂噬作用的分子機制、進而操弄脂噬作用已達保護神經之功效。
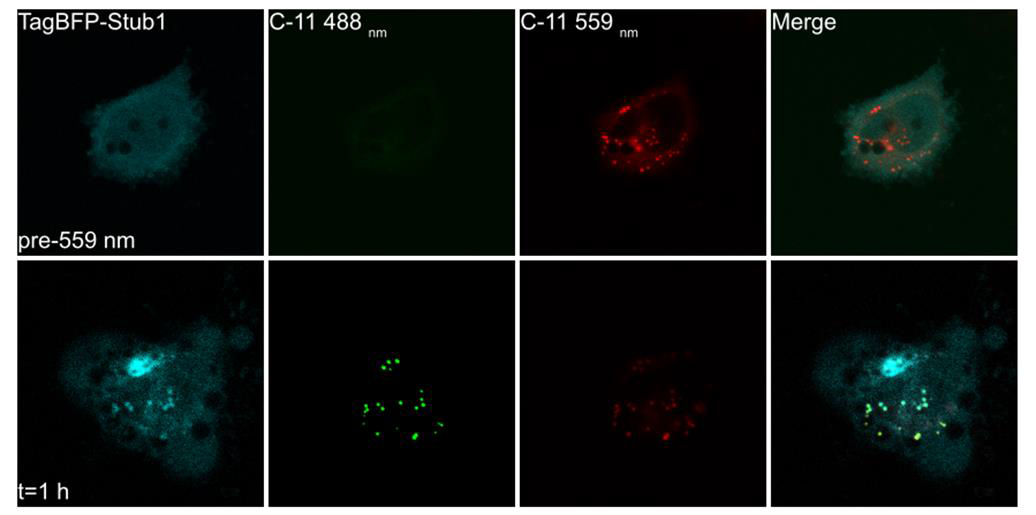
Figure. LD ROS drives Stub1 recruitment. Top row: before LD ROS generation, LDs displayed only red emission from BODIPY 581/591 undecanoic acid. Bottom row: after LD ROS generation for 1 hr (elicit by 559 nm illumination). LDs acquired BODIPY 581/591 undecanoic acid green fluorescence as well as Stub1.
Stub1, and ubiquitin E3 ligase, remained mostly cytosolic under basal conditions. Upon exposure to ROS, LDs acquired BODIPY 581/591 undecanoic acid green fluorescence and displayed Stub1 on their surfaces (Fig. 2). We are currently investigating this Stub1-mediated LD maintenance pathway. Interestingly, we have also recently reported that Stub1 quality controls ROS-stressed peroxisomes [Chen BH, Chang YJ, Lin S, and Yang WY*, Hsc70/Stub1 promotes the removal of individual oxidatively stressed peroxisomes, Nature Communications, 11, 5267, (2020).
我們近期研究成果發現Stub1會調節由氧化壓力所引起的過氧化物酶體的品質,因此調節油滴之平衡 (發表於2020 Nature Communications)。