上皮卵巢癌(OC)中Period2 (PER2)增強子之選擇使用與分層3D基因組結構、上皮間質轉化(EMT)以及細胞外基質(ECM)重編程之關聯
Alternative PER2 (Period2) enhancer usage in epithelial ovarian cancer (OC) and the functional consequences in 3D genome structure, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling.
計畫主持人:臺大-醫學系 黃韻如、中研院-基因體中心 黃雯華
PER2在Epi-A卵巢癌中的關鍵抑癌作用與治療策略
本研究揭示PER2在Epi-A卵巢癌(OC)亞型中發揮關鍵的腫瘤抑制作用,對疾病進程與治療反應具有重要影響。臨床分析顯示,PER2高表達的Epi-A OC患者擁有顯著較佳的無病生存期與總生存期,相較之下,PER2低表達的患者預後較差,突顯其在維持腫瘤細胞穩定性中的重要性。
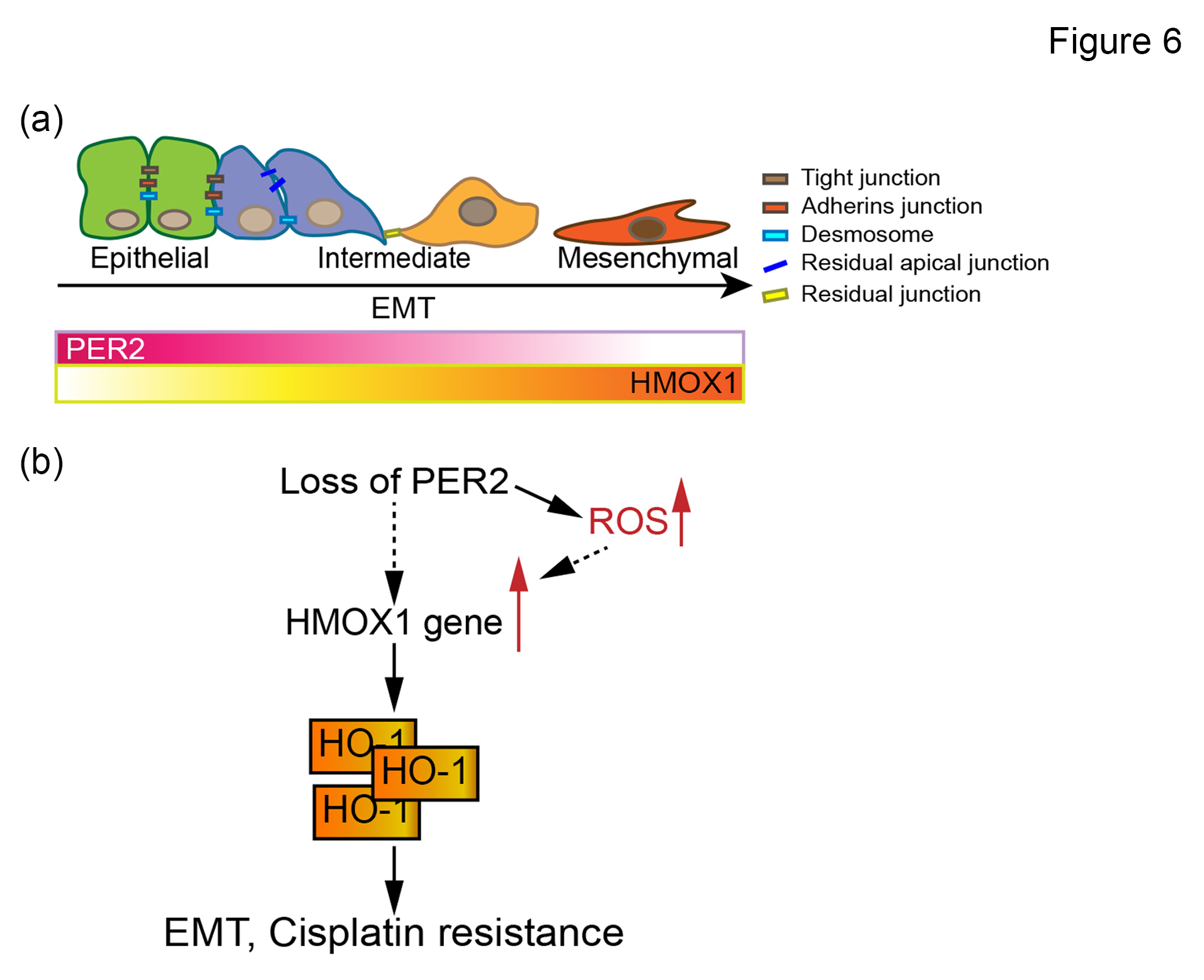
機制研究進一步證實,PER2下調直接促進上皮-間質轉化(EMT),導致癌細胞遷移與侵襲能力增強。這一現象與Heme oxygenase-1 (HMOX1/HO-1) 的顯著上調密切相關,而HO-1作為氧化壓力與腫瘤進展的核心調控因子,顯示PER2可能透過HO-1抑制EMT以維持細胞上皮態,從而發揮抗腫瘤作用。
此外,我們發現PER2下調顯著增強Epi-A OC 細胞對順鉑(cisplatin)的抗藥性,進一步確立其在化療反應中的關鍵角色。值得關注的是,藥理學抑制HO-1可有效阻斷因PER2缺失所導致的惡性轉變,降低細胞遷移與侵襲能力,同時恢復順鉑敏感性。這一結果不僅確認HO-1為PER2調控EMT與化療反應的核心下游因子,也提供了HO-1作為治療靶點的強力證據。
綜合而言,本研究首次揭示PER2-HMOX1/HO-1在EMT調控與化療敏感性中的關鍵作用,並提供明確的分子機制依據。我們的研究強調,透過維持PER2表達或精準靶向HO-1,可作為有效抑制腫瘤進展並增強化療效果的策略,為Epi-A卵巢癌患者提供嶄新的治療方向。
The Critical Tumor-Suppressive Role of PER2 in Epi-A Ovarian Cancer and Its Therapeutic Potential
Our study establishes PER2 as a key tumor suppressor in the Epi-A ovarian cancer (OC) subtype, demonstrating its crucial impact on disease progression and therapeutic response. Clinical analysis reveals that Epi-A OC patients with high PER2 expression exhibit significantly better disease-free survival and overall survival, whereas those with low PER2 expression have poorer prognoses, underscoring its essential role in maintaining tumor stability.
Mechanistically, our findings confirm that PER2 downregulation directly promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), leading to enhanced cancer cell migration and invasion. This effect is strongly associated with the upregulation of Heme oxygenase-1 (HMOX1/HO-1), a central regulator of oxidative stress and tumor progression. These results suggest that PER2 exerts its tumor-suppressive function by inhibiting HO-1, thereby maintaining an epithelial-like phenotype and preventing EMT.
Furthermore, we demonstrate that PER2 depletion significantly enhances cisplatin resistance in Epi-A OC cells, further emphasizing its role in chemoresponse. Notably, pharmacological inhibition of HO-1 effectively reverses PER2 depletion-induced malignancy, suppressing cancer cell migration and invasion while restoring cisplatin sensitivity. This finding not only identifies HO-1 as a critical downstream effector of PER2 but also establishes it as a promising therapeutic target.
In summary, our study uncovers the essential regulatory axis of PER2-HMOX1/HO-1 in EMT and chemoresistance, providing strong mechanistic evidence for its role in Epi-A OC progression. We propose that maintaining PER2 expression or selectively targeting HO-1 represents a viable strategy to suppress tumor progression and enhance chemotherapy efficacy, offering a novel therapeutic avenue for Epi-A OC patients.
