創新穩定蛋白之小分子並用於探討龐貝氏症的治療效果
Discovery of novel protein stabilizers: Study of their efficacy toward Pompe disease
計畫主持人:臺大醫學系-胡務亮、中研院基因體中心-鄭偉杰
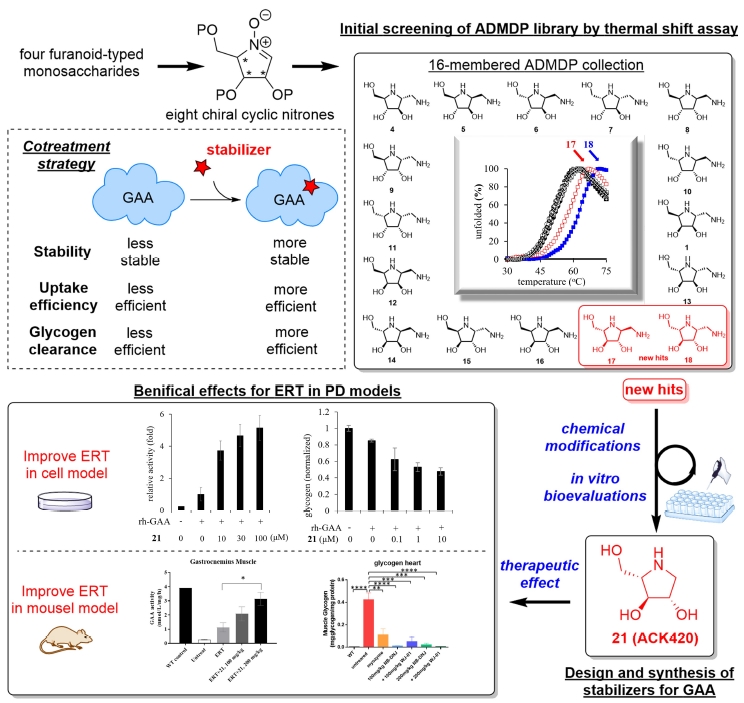
In this project, we utilized the unique polyhydroxylated pyrrolidine-based in-house chemical library consisting of all sixteen synthetic ADMDP (1-aminodeoxy-DMDP) stereoisomers (structurally covering four chiral centers, three hydroxy groups, one aminomethyl group in each stereoisomer) to study the GAA protein stability via the thermal shift assay. To our delight, two initial hits possessing the (3S,4S,5S) configuration pattern (L-arabino typed), were found. Diversification at the C2 position was performed by using natural product-inspired combinatorial chemistry (NPICC) to develop several D- and L-arabino typed iminosugars and a 300-membered amide Library.
Through our efforts, one unnatural polyhydroxylated pyrrolidine 21 was found to be the most potent and effective GAA stabilizer, suppressing GAA inactivation in enzymatic or cellular platforms. Co-treatment of 21 with rh-GAA in PD cells can not only enhance the GAA activity but also reduce the glycogen content, compared to the rh-GAA treatment (ERT) only. The durability of enzyme activity in PD cells indicated that co-treatment is able to prolong therapeutic activity and potentially amend PD patient treatment. The enhancement effect was also found in the early proof of concept animal study, suggesting the therapeutic potential of co-treatment of 21 and rh-GAA.
We provided (1) the design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of enzyme stabilizing activity of polyhydroxylated pyrrolidines for GAA, (2) molecular modifications of polyhydroxylated pyrrolidines that lead to a significantly improved understanding of their structure-activity relationships (SAR) toward GAA stabilization, (3) computational studies that analyze the SAR of polyhydroxylated pyrrolidines toward the stabilization of GAA. These results will inspire medicinal chemists to prepare libraries with chiral diversity and the used of pyrrolidine-based iminosugars as enzyme stabilizers for other disease-associated enzymes. In this study, we emphasize the chemistry strategy instead of pharmacology-oriented study, and would like to inspire scientists to think about how to create scaffolds, molecules, and libraries as well as their structural diversity including core diversity, configuration diversity, and substituent diversity. Thus, we still think our work is suitable for publication in Medicinal chemistry-oriented journals.
This is the first study to demonstrate improvements in the efficacy of enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) by adding a pyrrolidine-based small molecule into GAA in vivo, and sheds light on the discovery of pyrrolidine-based GAA stabilizers initially from the unique pyrrolidine-based natural product-inspired chemical space. We do believe our chemistry and the developing strategy of protein stabilizers will inspire other scientists and chemists to discover other new small molecules as protein stabilizers toward other disease-associated enzymes.
在本計畫中,我們利用由16 個分子所組成的多羥基吡咯烷立體異構物分子庫來進行熱轉移分析研究 GAA 的穩定性。我們從中發現了兩個具有(3S,4S,5S)立體化學特性(L-arabino 類型)的有效分子,隨後通過使用天然產物啟發的組合化學 (NPICC) 進行 C2 位置的多樣化,並開發出數種 D-和 L-阿拉伯醣類型的亞胺醣和一個300 個分子所組成的分子庫。
經過酵素實驗的分析,一種非天然的多羥基吡咯烷 21 被發現是最有效的 GAA 穩定劑,可抑制GAA 在不同平台的失活現象。與僅用 rh-GAA 投藥 (ERT) 的細胞相比,21 與rh-GAA 對 PD 細胞進行混合投藥不僅可以增強 GAA 在細胞中的活性,還可以降低細胞中的肝醣含量。 PD 細胞中酶活性的持久性也證明混和投藥能夠延長有效GAA 活性並可應用於提升 PD 患者的治療效果。在動物模型中也發現了酶活性的增強現象,證明 21 和 rh-GAA混合投藥的治療方式是有潛力的。
我們提供了 (1) 多羥基吡咯烷對 GAA 的酶穩定活性的設計、合成和生物活性評估,(2)藉由多樣性的多羥基吡咯烷的分子庫,我們對於小分子和GAA 的構效關係 (SAR) 有更進一步的了解, (3) 分析多羥基吡咯烷的 SAR 對 GAA 穩定性的理論計算研究。這些成果將啟發更多的藥物化學家製備具有對掌性和多樣性的分子庫,並使用吡咯烷類的亞胺醣作為其他疾病的酶穩定劑。