泛素化於溶小體功能與品管的影響
Selective ubiquitination in lysophagy, lysosome maintenance, and lysosomal disorders
計畫成果摘要
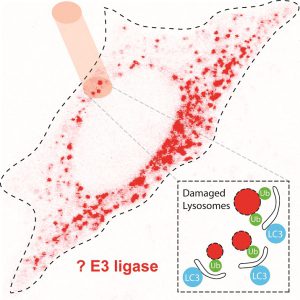
泛素化被認為是控制受質被細胞自噬分解的關鍵。我們在先前的實驗已經發現,受損的溶小體會被泛素化,接著被細胞自噬蛋白辨識,最後進而被分解。但是負責將受損的溶小體泛素化的泛素蛋白酶目前尚未被發現。利用這個計畫的資助我們試圖利用APEX的方式來找出可能幫助受損的溶小體泛素化的泛素蛋白酶。目前我們已經找出幾個可能的泛素蛋白酶,所以將會在未來利用各種實驗方法驗證他們在受損的溶小體被泛素化中扮演的確切角色。
Project abstract
Ubiquitination has been implicated as a key signal for the selective degradation of substrates through autophagy. We have previously discovered that damaged lysosomes undergo selective ubiquitination, recruit autophagic adaptors, and are eventually turned over through that autophagic pathway (termed lysophagy). It however remains unknown what ubiquitin ligases mediate this degradation pathway. With the help of this grant and others we attempted to develop an APEX-based strategy to identify the ubiquitin ligases involved. Using this strategy we identified a panel of candidates that may be responsible for lysophagy. These candidates will be subjected to future testing for complete understanding of the lysophagy pathway.