肝病奈米組合藥物研發
Combination Nanotherapy of Liver Diseases
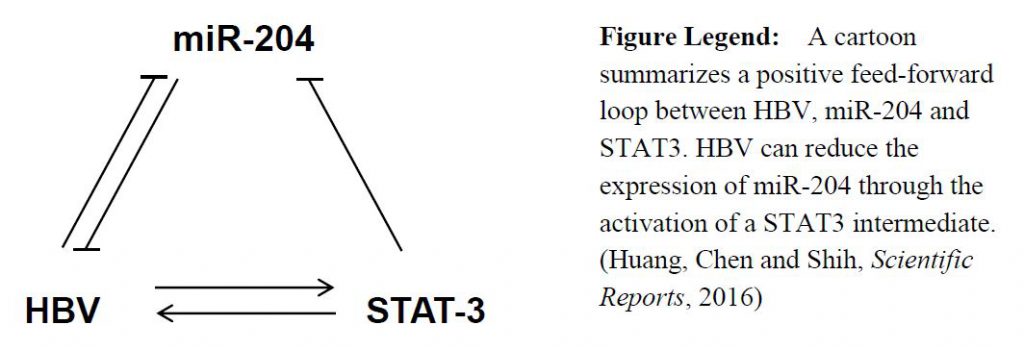
B型肝炎病毒(HBV)在感染人類的病原之中佔大宗。在本次實驗中,我們發現到在HBV表現的細胞中有兩個微小核醣核酸(micro-RNA; miR): miR-204及miR-1236的表現量下降,而且發現到這兩個miRNA能回過頭來抑制HBV的複製。我們利用生物資訊的方法以及reporter實驗找到了miR-1236透過結合到HBV的特定mRNA區域來抑制HBV的複製及蛋白質生成 。而另一方面,由生物資訊方法找到的miR-204則無法抑制HBV的RNA及蛋白質生成。但意外地,我們找到了miR-204能夠抑制HBV 前基因體(pregenomic) RNA的包裝(encapsidation)及病毒衣殼 (capsid) 的組裝。我們更進一步證實HBV透過活化宿主轉錄因子STAT3來抑制miR-204的表現量,驗證了HBV, miR-204及STAT3三者之間存在一個正向調控的路徑。有趣的是,miR-204已經在某些發表的文章中被認為是能夠抑制腫瘤的因子(tumor suppressor),由於慢性B型肝炎的患者罹患肝癌的機率相對地高,我們推測HBV抑制miR-204的現象或許是促進肝癌發生的原因之一。在我們的研究中找到的兩個抑制HBV的miRNA: miR-204以及miR-1236,這兩者或許能透過新發展的微流體系統(microfluidic systems)技術,高通量地找尋出合適且能應用於治療HBV的合併療法。
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a major human pathogen. In this study, we found that miR-204 and miR-1236 were down-regulated in HBV-producing cells, and each could suppress HBV replication. Using a bioinformatic approach and a reporter assay, we identified miR-1236, which can reduce HBV replication and protein production by directly targeting at HBV specific mRNA. In contrast, miR-204 was identified by a microarray approach, and had no effect on HBV RNA and protein production. Surprisingly, miR-204 could inhibit HBV pregenomic RNA encapsidation and capsid assembly. We further demonstrated that HBV suppressed miR-204 expression via activating a host transcription factor STAT3. We established a positive feed-forward loop between HBV, miR-204 and STAT3. Interestingly, miR-204 has been considered as a tumor suppressor in some literature. Since the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is significantly increased in chronic HBV patients, it is possible that chronic suppression of miR-204 by HBV contributes to HCC incidence. Both miR-204 and miR-1236 might be useful for developing optimized combination therapy against HBV with the newly developed microfluidic systems for high throughput optimization.