開發運用人工智慧篩選可降解新興環境有機污染物如阻燃劑微生物之新穎技術
Develop a novel methodology to screen microbial degraders for emerging contaminants such as flame retardants by artificial intelligence
國立臺灣大學農業化學系 施養信 教授
中央研究院資訊所 林仲彥 研究員
計畫執行期間:2023.1.1 – 2024.12.31
優良研究成果
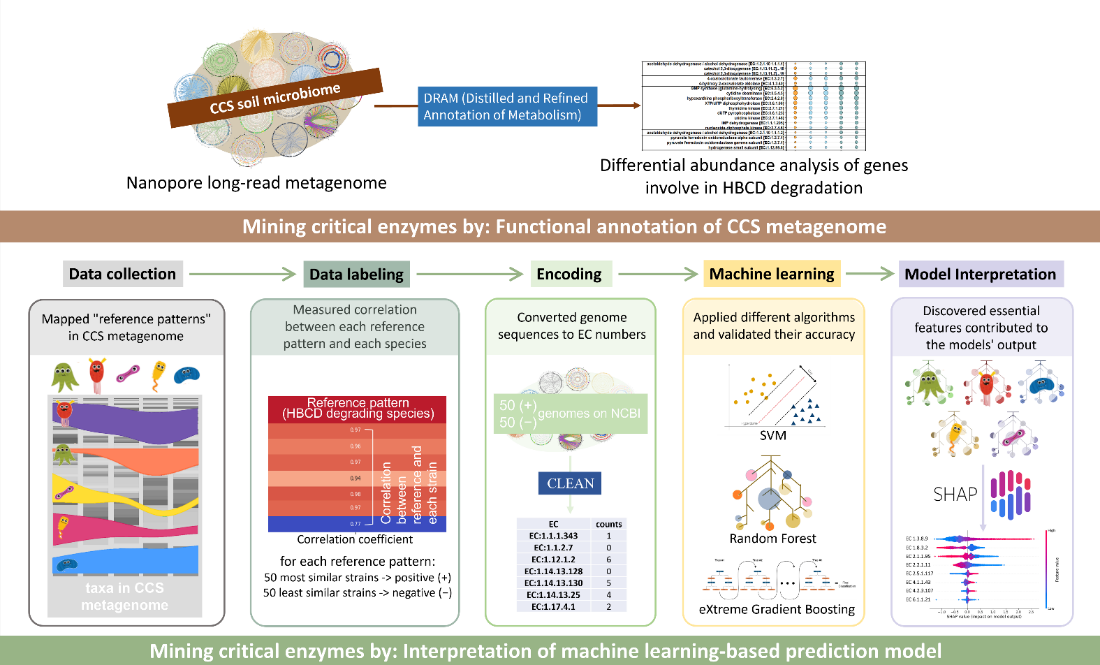
結合機器學習模型和功能性微生物基因組策略來鑑別可降解六溴環十二烷的關鍵基因群 (Interpretation of Machine Learning-Based Prediction Models and Functional Metagenomic Approach to Identify Critical Genes in Hexabromocyclododecane Degradation)
六溴環十二烷 (Hexabromocyclododecane, HBCD) 是持久性有機污染物(persistent organic pollutants, POPs)中的一種,對環境造成嚴重風險。透過微生物降解處理 HBCD 污染是一個環境友善且有效的解決方案,但尋找有效的微生物和其對應基因一直是一個耗時且耗費資源的過程。臺灣大學施養信與中研院林仲彥研究團隊合作研究透過功能性分析學和機器學習,分析環境總體基因體資料,尋找參與 HBCD 降解的關鍵基因。
本研究透過機器學習模型發現了兩個與減少HBCD降解有關的基因:硫醇氧化酶thiol oxidase, EC 1.8.3.2), 苯基丙酮酸脫羧酶(phenylpyruvate decarboxylase, EC 4.1.1.43)和 假尿苷激酶(pseudouridine kinase EC 2.7.1.83)則與降解效率呈正相關。儘管機器學習模型與功能性註釋分析所發現的確切酵素有所不同,但整體代謝途徑密切相關。這種結果可能源自於,功能註釋往往專注於對 HBCD 降解有正面影響的基因,但機器學習可以同時顯示對 HBCD 降解有正面和負面影響的基因。
作為首個應用機器學習於總體基因體數據以理解環境有機汙染物如POPs環境降解的研究,這些結果提供了對微生物動態的全面了解。本研究將有助於開發更有效的 POPs等難分解有機污染物污染清理策略,改善我們解決這個POPs的能力。
- Li, Y.-J., Chuang, C.-H., Cheng, W.-C., Chen, S.-H., Chen, W.-L., Lin, Y.-J., Lin, C.-Y., & Shih, Y.-H. (2022). A metagenomics study of hexabromocyclododecane degradation with a soil microbial community. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 430, 128465. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128465
- Lin, Y.-J., Hsieh, P.-H., Mao, C.-C., Shih, Y.-H, Chen, S.-H., Lin, C.-Y. (2025) Interpretation of Machine Learning-Based Prediction Models and Functional Metagenomic Approach to Identify Critical Genes in HBCD Degradation. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 486, 136976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.136976